Building the D2C Capability
Along with understanding market readiness, CPGs must ensure they have capabilities in place to launch a D2C model and scale it efficiently. There are three core enablers required for capturing direct and indirect value from D2C opportunities:
A global D2C technology platform: A D2C technology platform is a three-tiered system that provides a foundation for scaling D2C programs. A set of global capabilities exists at its core, with the ability to layer on brand and geographic-specific extensions, giving flexibility to build based on market needs and opportunity. A platform approach reduces time-to-market and lowers technology costs by uniting the organization under one system.
An agile operating model: Along with strategy, getting the right governance model out across global, brand and geographic extensions is critical as the model scales. To plan effectively, CPGs should consider factors like resource allocation, budget, project approval, and overall strategy to determine appropriate stakeholders and prioritize implementation.
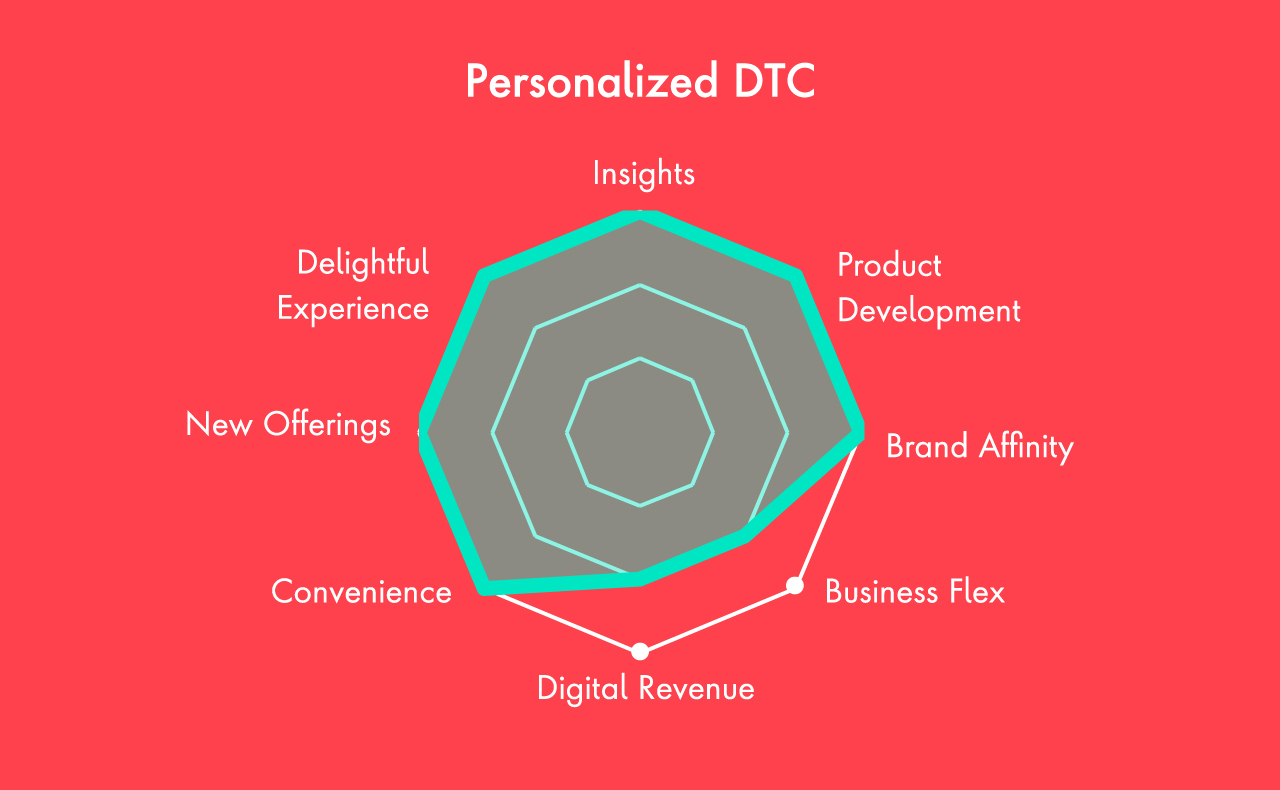
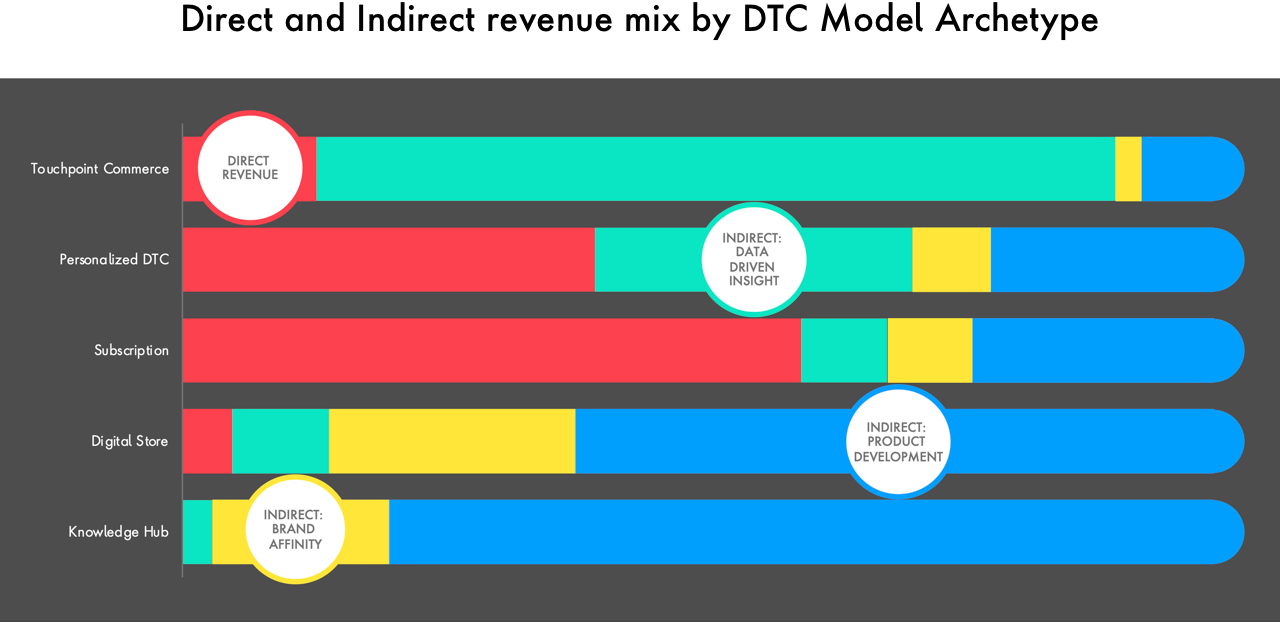
D2C data capture: Unlocking the full value of D2C requires companies have core capabilities to collect, analyze and understand consumer and marketing data and turn these into relevant, consistent and personalized insights and interactions. Having clear first-party D2C data capture standards and a strong integration with a global first-party data ecosystem is key to capture full indirect value.
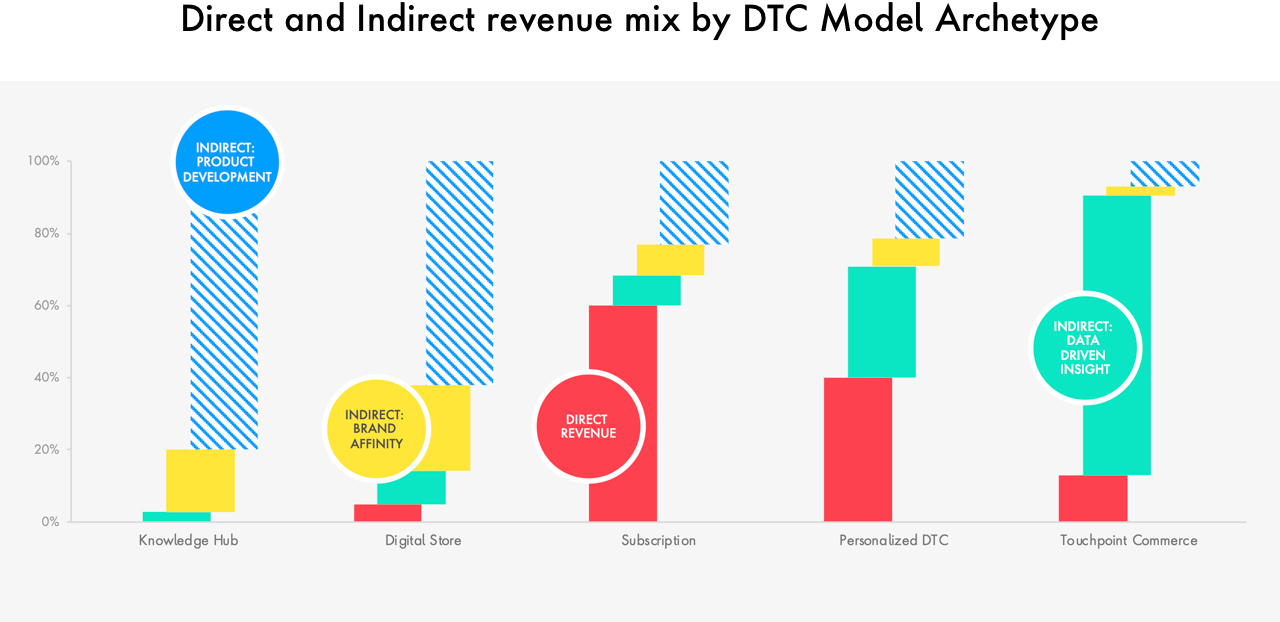
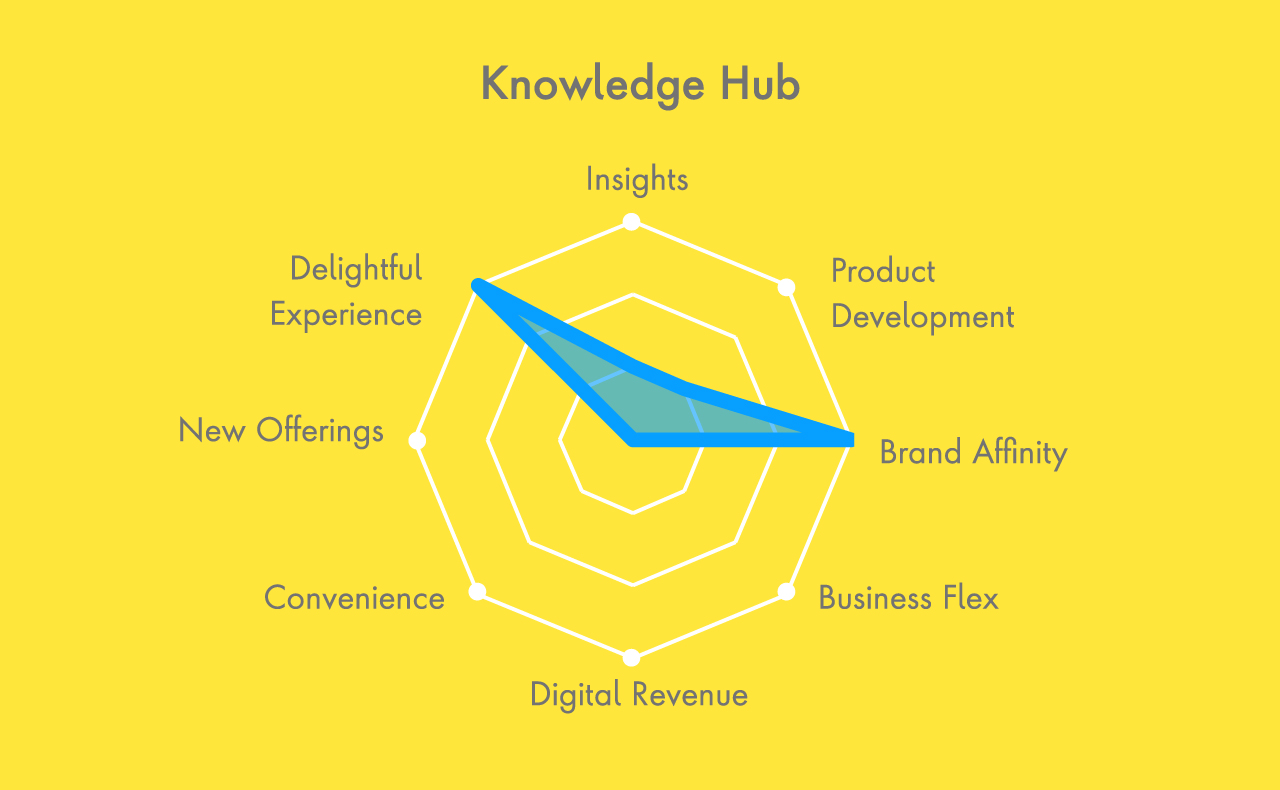
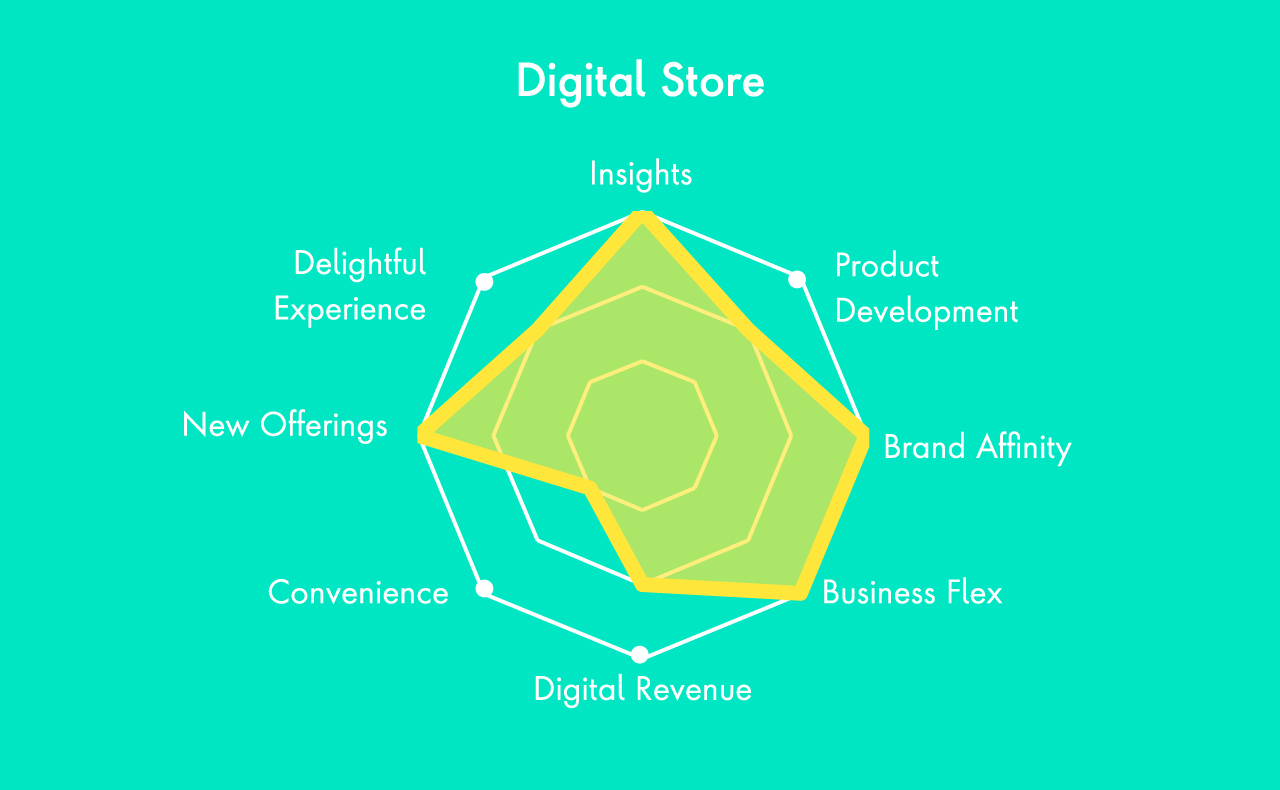
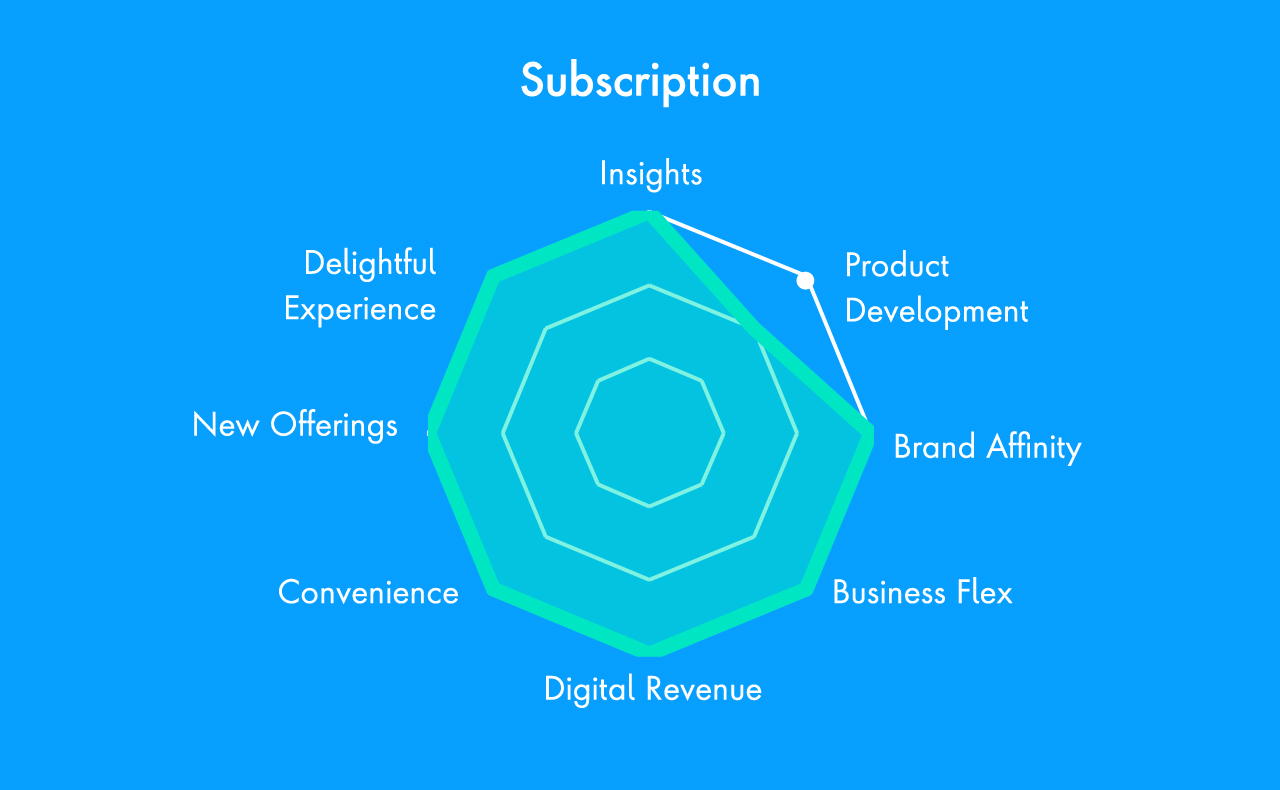
Choosing the Right D2C Model
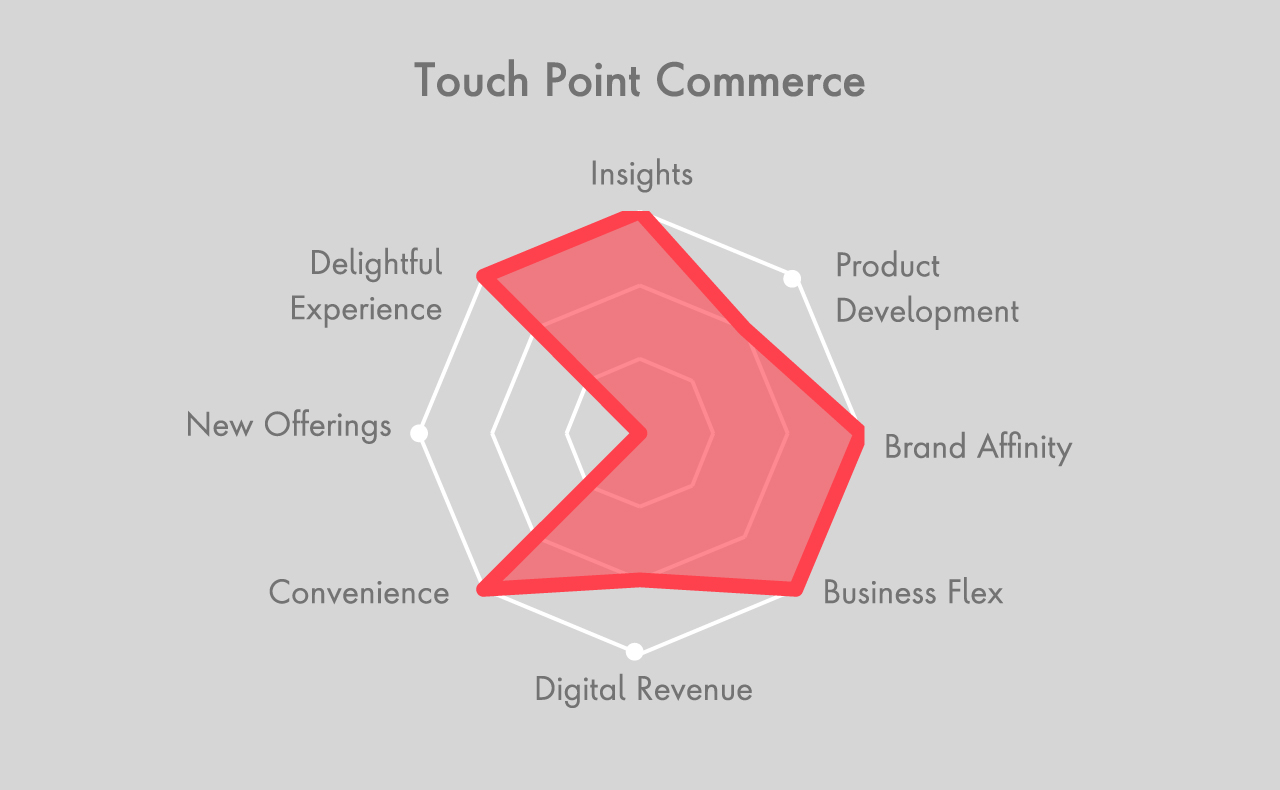
There are many opportunities for CPG firms to capitalize on the direct and indirect value that D2C has to offer, with some of the biggest companies leveraging different tactics to create new experiences unique to their brands today. For CPGs looking to get started, assessing business capability, market readiness, and digital maturity can uncover areas ripe for innovation. Supported by agile technology solutions, CPGs can then pave a path to implementation, establishing a longstanding D2C model that’s built to scale.